This is you on drugs
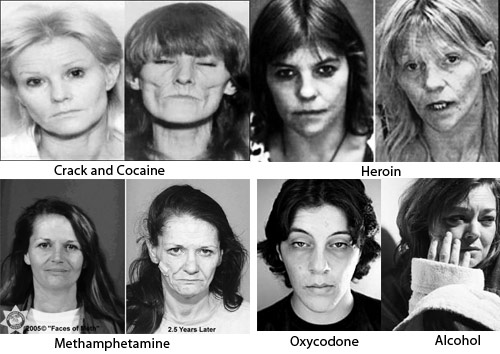
We're not here to tell you whether you should take drugs or not. You can make that choice on your own. But it is important that you know the short- and long-term effects of what you're putting in your body.
METHAMPHETAMINE
What it is
Methamphetamine is a central nervous system stimulant. It affects chemicals in the brain and nerves that contribute to hyperactivity and impulse control.
Short-term effects
- Meth's effect on brain chemistry can lead to violent behaviour
- "Tweaking," which includes anxiety, wakefulness and intensely focused attention, teeth grinding
- Hyperactivity, aggression and obsessive behaviour
- Psychotic behaviour, such as paranoia, hallucination and delusions
- Euphoria, extreme energy, lowered inhibitions, not sleeping for days, weight loss
Long-term effects
- Build up a tolerance to the drug, leading to anxiety, depression and the urge to increase doses
- Some users experience a sensation of bugs crawling across the skin, which may lead the user to pick at his or her face, leaving large scabs
- Impaired cognitive abilities, including memory, judgment, reasoning and motor coordination
— this damage may be permanent
- Changes brain chemistry, destroying the wiring in the brain's pleasure centres and making it increasingly impossible to experience any pleasure at all
- Studies have shown that these tissues can re-grow over time with clean living, but the repair may never be complete
- Puts users at high risk for viruses like HIV and hepatitis because it lowers inhibitions, leading some users to engage in unprotected sex or share needles
- Cardiovascular problems like rapid or irregular heartbeat, increased blood pressure and blood vessel damage than can result in stroke
- Tooth decay from tooth grinding, saliva deficiency and extreme lapses in hygiene
CRACK AND COCAINE
What it is
Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant. Cocaine in its powdered hydrochloride salt form can be snorted or dissolved in water and injected. Crack is cocaine that has been processed to make a rock crystal, which is heated to produce vapors that are smoked.
Short-term effects
- Increases levels of dopamine in the brain, creating feelings of euphoria.
- Increased energy, mental alertness
- Constricts blood vessels, dilates pupils, increases body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure
- Can cause headaches, abdominal pain and nausea
- Decreases appetite
Long-term effects
- Its effect on the way dopamine is transmitted and received can create changes in the brain
- Kidney damage
- Using increased amounts in an effort to prolong and intensify the high
- Snorting can lead to loss of sense of smell, nosebleeds, problems swallowing, hoarseness and a chronically runny nose
- Ingesting cocaine can lead to severe bowel gangrene due to reduced blood flow
- Sharing needles while injecting cocaine can lead to an increased risk of contracting HIV and other blood-borne diseases
- Paranoid psychosis, meaning auditory hallucinations and a loss of touch with reality
- Cocaine puts a huge strain on the cardiovascular system as it dramatically elevates the user's heart rate, and can lead to arrhythmia, heart attack and stroke
- Even recovered addicts are seven times more likely to have a heart attack than the average person
- Cocaine-related deaths are usually caused by cardiac arrest or seizure followed by respiratory arrest
OXYCODONE
What it is
Often sold under the brand name OxyContin, it is an opiate prescribed for moderate to severe pain. It is given in pill form, and is slow-acting. Some users crush and snort the pills, leading to a high that is reported to be more intense than that of heroin.
Short-term effects
- Reduced physical pain and muscle weakness
- Severe itching
- Nausea and constipation
- Depresses the central nervous system, which can lead to strange behaviour, lightheadedness, mental clouding, confusion, sleepiness or mood swings
- Dramatically slows breathing; if a person breathes fewer than 10 times per minute, he or she is at risk for permanent brain damage
Long-term effects
- Malnutrition and weight loss
- Arthritis and other rheumatologic problems
- Collapsed veins from intravenous use
- Liver and/or kidney disease
- Decreased levels of testosterone, which may result in impotence or enlargement of the prostate
- Changes brain chemistry and makes the brain think it needs the drug for normal function
- Users can build up a tolerance to oxycodone, leading them to ingest more to produce the same high as when they first started using
HEROIN
What it is
Heroin is a highly addictive drug made from processed morphine. It affects the brain's pleasure systems and interferes with the brain's ability to feel pain. The type of heroin that is often found on the streets ranges in color from white to dark brown. The color of heroin is affected by the impurities left behind during manufacturing. Heroin can be injected, smoked, sniffed or snorted.
Short-term effects
- Euphoria
- Dry mouth, flushing of the skin, heaviness of limbs
- After the euphoria stage ends, the user may experience an alternately wakeful and drowsy state where mental functioning becomes clouded
- Reduced pain
- Anxiety
- Nausea
- Hypothermia
- Breathing difficulties
Long-term effects
- Developing a tolerance can lead to using more frequently and higher doses
- Can lead to miscarriages, heart infections
- Increased risk of contracting HIV and hepatitis when sharing needles
- May lead to stroke, skin infections, collapsed veins and lung infections
- Withdrawal usually begins eight to 12 hours after the last dose; symptoms include restlessness, muscle and bone pain, diarrhea, vomiting and cold flashes
MARIJUANA
What it is
Marijuana is an herb that can be smoked or baked into food. It contains chemicals called cannabinoids; the best known is called tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The high caused by smoking marijuana is mainly due to THC.
Short-term effects
- Stimulates appetite and suppresses nausea
- Lowers pressure in the eye and is sometimes used to treat glaucoma
- Reduces muscle spasms in people with nerve problems
- Sometimes used as a treatment to reduce pain
- Can disrupt balance, physical coordination and visual perception, making it dangerous to drive while high
Long-term effects
- Linked to some of the same health issues as smoking tobacco, such as bronchitis, but has not clearly been linked to lung cancer
- Memory loss after prolonged periods of smoking marijuana, and the more a user smokes, the longer it takes to get his or her memory back to normal
- Psychological dependence gains strength over time, users smoke increasingly large quantities of marijuana in order to get the same feelings they did when they first started
- Impaired coordination, balance, reflexes and physical performance
— will improve after living clean
- Hallucinations, psychosis
- Impaired ability to learn, functioning at a lower intellectual level.
- Depression
- People who are prone to mental illness increase their risk of developing full-blown mental illness with heavy use
- Anxiety, panic attacks, feelings of discomfort
ALCOHOL
What it is
Alcohol is a depressant that is consumed as a beverage. Approximately 80 per cent of the alcohol in a beverage is absorbed in the small intestines and the remaining 20 per cent is absorbed in the stomach. The speed at which the alcohol is absorbed depends on the amount of alcohol consumed, whether the consumer's stomach is empty or full and the type of drink.
Short-term effects
- Slows breathing and heart rate
- Lowered inhibitions, which may lead to risky behaviour
- Poor coordination, slurred speech
- Blackouts and memory loss
- Nausea or vomiting, caused by distortion of the person's sense of balance or by the body's attempt to rid itself of the poison
- Stupor at a blood alcohol concentration of 0.40, which may include disorientation, confusion, severely impaired brain and muscular function
- Coma when the BAC reaches a level of 0.50, with a high risk of respiratory failure and death
- Hangovers and headaches Long-term effects
- Irritation of the stomach lining, which can be painful and is potentially fatal
- Tissue damage to the liver and pancreas
- Alcohol absuse can lead to — fatty degeneration in the liver, which can cause nausea and vomiting, lack of appetite, weight loss and fever
- Brain damage, which can lead to dementia, difficulties with coordination and motor control, and loss of feeling or painful burning in the feet
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Increased risk of liver, throat, breast and other cancers
- Alcohol dependence can result in clinical depression
- Mothers who drink alcohol during pregnancy may give birth to infants with fetal alcohol syndrome, which can include mental retardation and irreversible physical deformities.













